“Mastering the Command Line’’

1. ls — The most frequently used command in Linux to list directories
2. pwd — Print working directory command in Linux
3. cd — Linux command to navigate through directories
4. mkdir — Command used to create directories in Linux
5. mv — Move or rename files in Linux
6. cp — Similar usage as mv but for copying files in Linux
7. rm — Delete files or directories
8. touch — Create blank/empty files
9. ln — Create symbolic links (shortcuts) to other files
10. cat — Display file contents on the terminal
11. clear — Clear the terminal display
12. echo — Print any text that follows the command
13. less — Linux command to display paged outputs in the terminal
14. man — Access manual pages for all Linux commands
15. uname — Linux command to get basic information about the OS
16. whoami — Get the active username
17. tar — Command to extract and compress files in Linux
18. grep — Search for a string within an output
19. head — Return the specified number of lines from the top
20. tail — Return the specified number of lines from the bottom
21. diff — Find the difference between two files
22. cmp — Allows you to check if two files are identical
23. comm — Combines the functionality of diff and cmp
24. sort — Linux command to sort the content of a file while outputting
25. export — Export environment variables in Linux
26. zip — Zip files in Linux
27. unzip — Unzip files in Linux
28. ssh — Secure Shell command in Linux
29. service — Linux command to start and stop services
30. ps — Display active processes
31. kill and killall — Kill active processes by process ID or name
32. df — Display disk filesystem information
33. mount — Mount file systems in Linux
34. chmod — Command to change file permissions
35. chown — Command for granting ownership of files or folders
36. ifconfig — Display network interfaces and IP addresses
37. traceroute — Trace all the network hops to reach the destination
38. wget — Direct download files from the internet
39. ufw — Firewall command
40. iptables — Base firewall for all other firewall utilities to interface with
41. apt, pacman, yum, rpm — Package managers depending on the distro
42. sudo — Command to escalate privileges in Linux
43. cal — View a command-line calendar
44. alias — Create custom shortcuts for your regularly used commands
45. dd — Majorly used for creating bootable USB sticks
46. whereis — Locate the binary, source, and manual pages for a command
47. whatis — Find what a command is used for
48. top — View active processes live with their system usage
49. useradd and usermod — Add new user or change existing users data
50. passwd — Create or update passwords for existing users.
Learn more about each command's real-time use case :
1. ls — The most frequently used command in Linux to list directories.
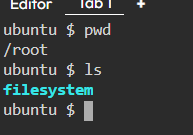
2. pwd — Print working directory command in Linux
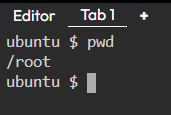
3. cd — Linux command to navigate through directories

4. mkdir — Command used to create directories in Linux

5. mv — Move or rename files in Linux

6. cp — Similar usage as mv but for copying files in Linux
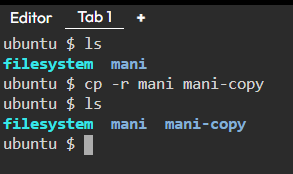
7. rm — Delete files or directories
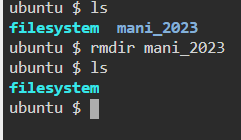
8. touch — Create blank/empty files

9. ln — Create symbolic links (shortcuts) to other files
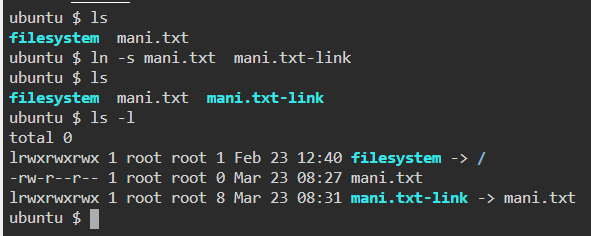
10. cat — Display file contents on the terminal

11. clear — Clear the terminal display

12. echo — Print any text that follows the command.

13. less — Linux command to display paged outputs in the terminal.

14. man — Access manual pages for all Linux commands ;
The man command in Linux is used to display the manual pages of Linux commands and other system functionalities.

15. uname — Linux command to get basic information about the OS

16. whoami — Get the active username
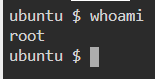
17. tar — Command to extract and compress files in Linux

18. grep — Search for a string within an output
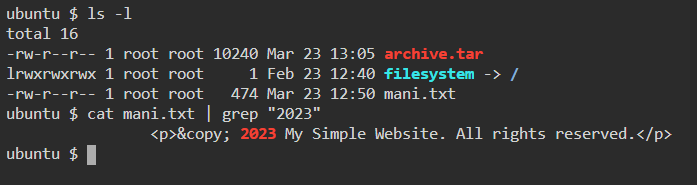
19. head — Return the specified number of lines from the top

20. tail — Return the specified number of lines from the bottom

21. diff — Find the difference between two files

22. cmp — Allows you to check if two files are identical.

23. comm — Combines the functionality of diff and cmp
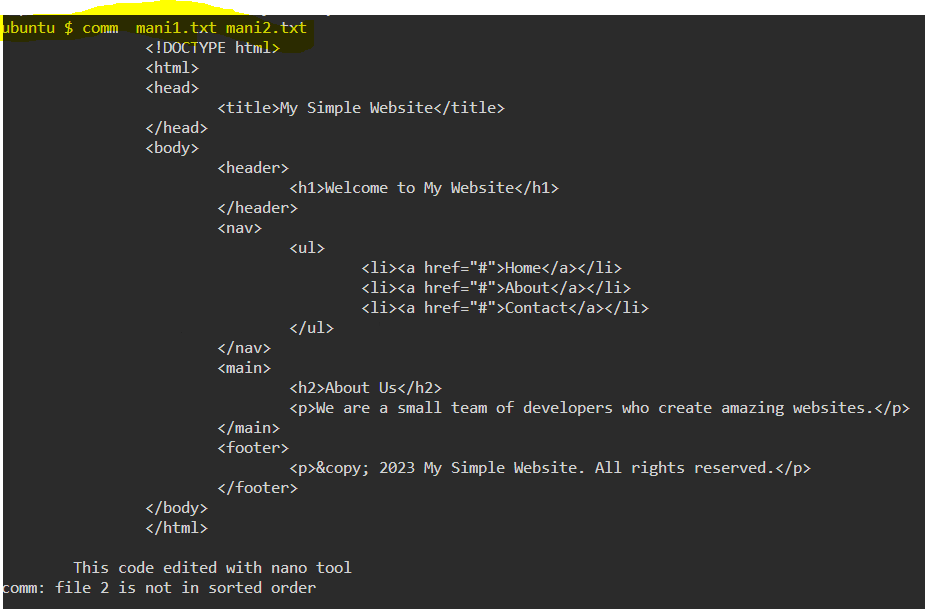
24. sort — Linux command to sort the content of a file while outputting

25. export — Export environment variables in Linux
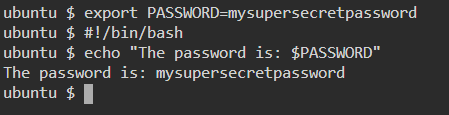
26. zip — Zip files in Linux

27. unzip — Unzip files in Linux
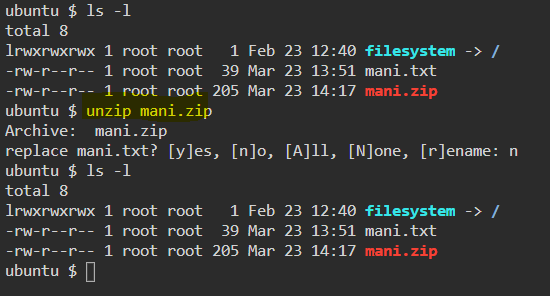
28. ssh — Secure Shell command in Linux
ssh username@hostname
29. service — Linux command to start and stop services
root@ubuntu:~ →> service ssh status
root@ubuntu:~ →> service ssh stop
root@ubuntu:~ →> service ssh start

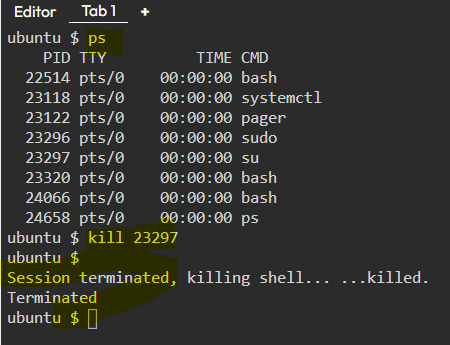
30. ps — Display active processes

31. kill and killall — Kill active processes by process ID or name
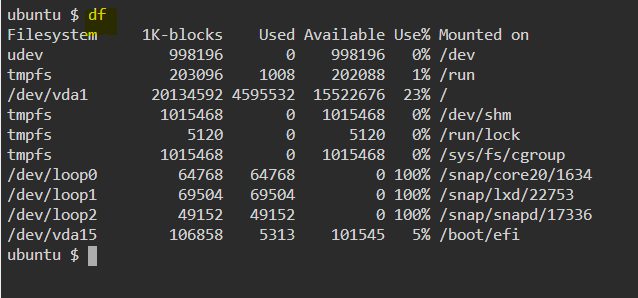
32. df — Display disk filesystem information
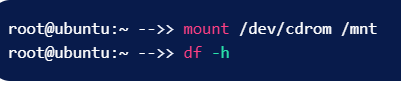
33. mount — Mount file systems in Linux.
34. chmod — Command to change file permissions
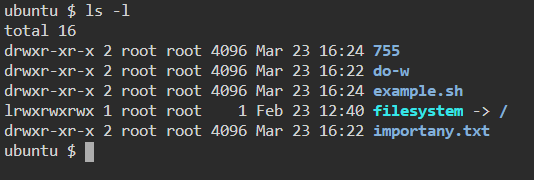
35. chown — Command for granting ownership of files or folders.
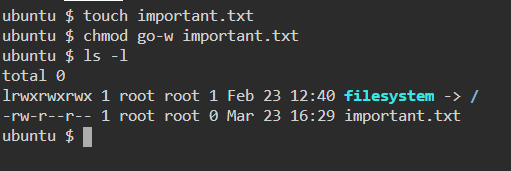
36. ifconfig — Display network interfaces and IP addresses
37. traceroute — Trace all the network hops to reach the destination

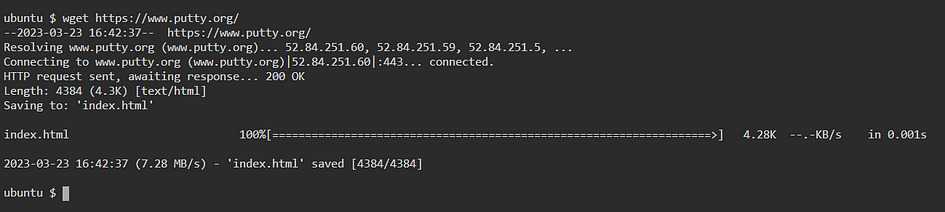
38. wget — Direct download files from the internet.
39. ufw — Firewall command

40. iptables — Base firewall for all other firewall utilities to interface with

41. apt, pacman, yum, rpm — Package managers depending on the distro.
Debian and Debian-based distros — apt install <package name>
Arch and Arch-based distros — pacman -S <package name>
Red Hat and Red Hat-based distros — yum install <package name>
Fedora and CentOS — yum install <package>
42. sudo — Command to escalate privileges in Linux.

43. cal — View a command-line calendar.

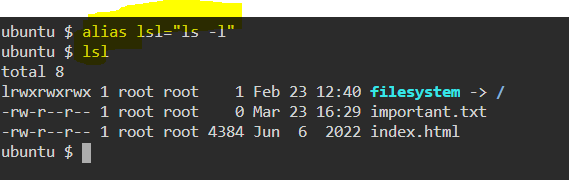
44. alias — Create custom shortcuts for your regularly used commands.
45. dd — Majorly used for creating bootable USB sticks
46. whereis — Locate the binary, source, and manual pages for a command.

47. whatis — Find what a command is used for

48. top — View active processes live with their system usage

49. useradd and usermod — Add new user or change existing users data.

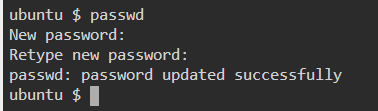
50. passwd — Create or update passwords for existing users.
Credits : digitalocean
https://github.com/gefkkd/-Mastering-the-Command-Line-.git
That’s it, thank you for reading.
👉 In case you would like to continue the discussion, you can always reach out to me on Twitter or on LinkedIn for professional networking, if you feel like following me on GitHub you can also do that.
👉 Follow Cloudnloud Tech Community for more insightful knowledge & resources & CloudnLoud YouTube channel.